Smart faucet integration is emerging as a practical extension of digital building systems rather than a novelty feature. In residential, multifamily, and light commercial environments, Internet of Things (IoT)–enabled faucets provide data that supports water efficiency, operational reliability, and proactive maintenance. For architects, engineers, and specification professionals, understanding how smart faucets interface with building systems is essential when planning for long-term performance and lifecycle management.
Industry studies indicate that IoT-enabled predictive maintenance can reduce unplanned downtime by up to 30% and lower maintenance costs by 15–25%. By integrating smart faucets with real-time monitoring sensors and building management systems, facilities can detect leaks, abnormal flow rates, and component wear early—improving water efficiency, operational reliability, and long-term asset performance.

What Defines a Smart Faucet in Building Systems
A smart faucet incorporates sensors, electronic controls, and connectivity that allow operational data to be collected and analyzed. Unlike conventional faucets, smart systems do more than regulate flow—they generate information about usage patterns and system health that can be used for monitoring and maintenance planning.
- Usage frequency and duration tracking
- Flow volume measurement
- Temperature monitoring
- Error and fault detection
- Remote diagnostics and alerts
IoT Architecture in Faucet Systems
Smart faucets function as endpoints within a broader IoT architecture. Data gathered from fixture level is transmitted through wired / wireless networks to centralized the platforms for reporting and analytics related services.
Key System Components
- Embedded sensors as well as solenoid valves
- Control modules with help of onboard firmware
- Power sources that is batteries or low-voltage connections
- Gateways along with building management systems (BMS)
- Cloud-based analytics.
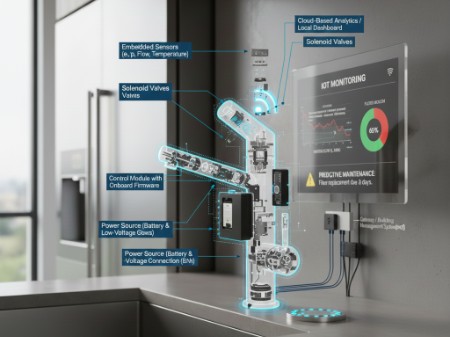
Monitoring Water Use and Performance
A key advantage of IoT-enabled faucet is it’s real-time monitoring. The live data collection can assist stakeholders understand how flow of fluid is used at the fixture level and point out performance related problems before hand.
- Identifying abnormal water flow patterns or leaks
- Comparing actual use against design assumptions
- Supporting fluid flow efficiency reporting
- Verifying performance of low-flow designs in practice.
This real time data can also support more accurate operations along with planning and can provide measurable feedback for sustainability related strategies.
Predictive Maintenance and Lifecycle Management
Instead of waiting for the visible failure, smart faucets are able to signal when components are nearing the service thresholds.
- Increased activation cycles approaching cartridge life limits
- Solenoid response delays indicating wear or obstruction
- Temperature instability suggesting mixing or supply issues
- Battery voltage trends supporting planned replacement timing
Touchless Faucets as the Foundation of Smart Integration
Touchless (sensor-activated) faucets are able to provide a natural entry point for IoT integration because they already rely on sensors as well as electronic control. This makes it very easy to add monitoring and diagnostics without changing users behavior.
Touchless faucet categories that demonstrate these system-level capabilities can be reviewed at FontanaShowers Commercial Sensor Faucets. General technical background on automatic faucet operation is available at Automatic Faucet.
Data Security and System Reliability Considerations
For AEC experts, smart faucet specification needs to be addressed reliability and data integrity alongside functionality.
- Secure data transmission protocols
- Clear separation between operational data and personal data
- Fail-safe operation during connectivity loss
- Local manual override functionality where appropriate
Integration with Building Management Systems
Smart faucets integrate with building platforms to support holistic fluid as well as energy management. When connected straight to a coordinated strategy, fixture data can complement metering, leak detection, and system analytics.
- Linking faucet data with water meters and leak detection systems
- Coordinating with hot water system monitoring
- Supporting compliance reporting for sustainability programs
- Providing inputs for digital twins and building analytics
Material and Hardware Durability in Smart Systems
Electronic capability doesn’t just remove the requirement for durable physical development. Smart faucets must still meet water exposure, cleaning, and activation-cycle demands while protecting electronic components.
- Lead-free brass or stainless steel construction
- Sealed electronic enclosures resistant to moisture
- Components rated for high activation cycles
- Compatibility with approved cleaning protocols
Material and compliance documentation relevant to electronic faucet systems can be reviewed at FontanaShowers Faucets Materials and Compliance.
Reviewing Smart Faucet Categories and System Context
Evaluating diverse faucet types assists designers to understand how IoT functionality is implemented across diverse platforms and applications while supporting the system-level research instead of just product-driven decisions.
The related resources consist of bathroom-sink-faucet.com, FontanaShowers, Commercial Sensor Faucets, BathSelect, and JunoShowers.
Conclusion
The integration of smart faucets marks the end of passive plumbing fixtures and signifies the beginning of actively data-producing architectural elements. With the help of IoT tracking and the capability of predictive maintenance, faucets are able to contribute to water savings.
As a resource for those interested in bathroom-sink-faucet.com, smart faucet viewed as a total building system, rather than individual products, is a means of making intelligent decisions.
References
- Building IoT and Facilities Management Monitoring Practices
- Predictive Maintenance and Lifecycle Management Concepts for Plumbing Fixtures
- Plumbing Materials, Electronics Protection, and Compliance Documentation